The United States is grappling with a severe housing affordability crisis, leaving many aspiring homeowners adrift in a turbulent market. Over the last few decades, the price of new single-family homes has skyrocketed, driven by a myriad of factors such as increasing labor and material costs, but land-use regulations and NIMBY policies have also played a significant role. These regulations limit the ability of builders to create affordable housing, ultimately contributing to a growing homeownership gap that affects millions. As a result, the construction industry faces considerable challenges, struggling with decreased productivity and stifled innovation. To address the pressing housing market challenges, it’s imperative to reassess the regulatory framework governing land use and explore solutions that facilitate the availability of affordable homes for everyone.
The current situation in the housing sector can be described as a dire predicament where affordability struggles plague potential buyers across the nation. This dilemma, often characterized by restrictive land-use regulations and unyielding community opposition, inhibits the development of necessary housing units. Consequently, the resultant scarcity of affordable options has widened the homeownership gap, casting a shadow over the American dream. With construction productivity lagging behind other industries, addressing these underlying issues has never been more crucial for restoring balance to the housing market. By confronting these challenges head-on, it may be possible to forge a pathway toward more accessible housing solutions for future generations.
Understanding the Housing Affordability Crisis
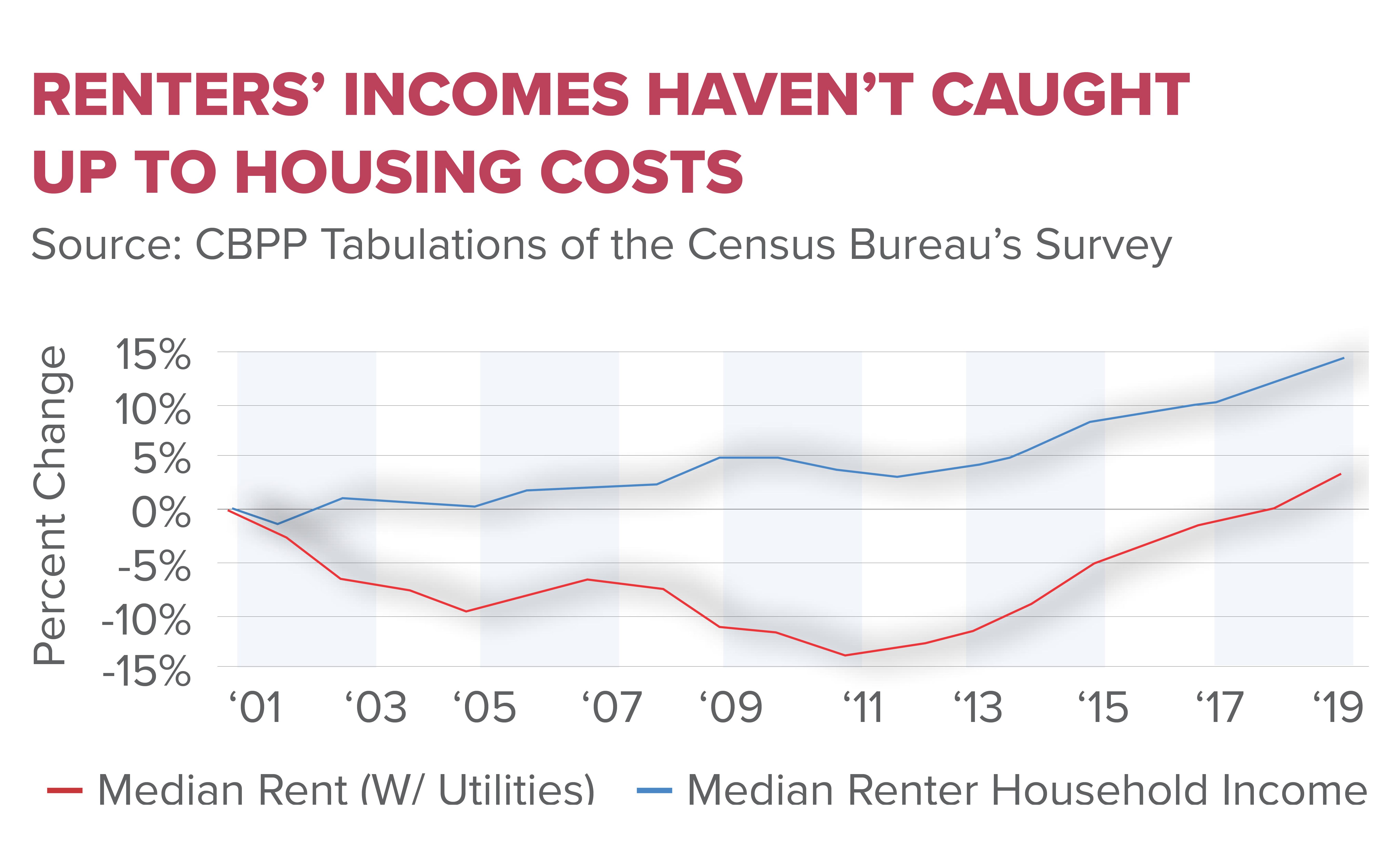
The housing affordability crisis in the United States has escalated to alarming levels, rendering homeownership unattainable for a significant portion of the population. A variety of factors contribute to this predicament, with the rising costs of new homes being the most apparent. Since 1960, the price of new single-family homes has more than doubled, influenced by escalating labor and material costs. However, a critical yet often overlooked contributor is the restrictive land-use regulations that govern where and how homes can be built. These regulations often impede large-scale developments, exacerbating the scarcity of affordable housing options.
In recent studies, economists argue that the linkage between housing affordability and land-use policies is undeniable. The prevalence of NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) attitudes leads to stringent zoning laws, which restrict the number of homes that can be constructed in desirable areas. This boundary on development not only stifles construction productivity but also contributes to the widening homeownership gap. The result is a housing market that is increasingly out of reach for middle and low-income families, thereby worsening the overall affordability crisis.
The Impact of Land-Use Regulations on Housing Supply
Land-use regulations have a considerable impact on housing supply, particularly in urban areas where demand for housing is high. These regulations often require developers to navigate complex approval processes, which can delay projects and drive up costs. Consequently, the size of residential projects has diminished over the years, leading to smaller firms that may lack the capacity for innovative building techniques associated with larger, more productive enterprises. This trend ultimately results in fewer homes being built, further restricting the supply amidst growing demand.
Additionally, research shows that as land-use regulations have increased in complexity and volume, the productivity of the construction sector has significantly declined. When builders are limited to smaller projects, they lose the economies of scale that could otherwise help lower construction costs. This stagnation in construction productivity means fewer affordable housing units enter the market, intensifying the struggles faced by prospective homeowners in a challenging housing market.
NIMBYism and Its Role in Housing Market Challenges
The phenomenon of NIMBYism presents significant challenges to the housing market, manifesting as local opposition to new developments. Residents often resist changes to their neighborhoods, fearing increased density, traffic, or disruption to their way of life. This opposition can stymie new housing projects, creating an environment where scarcity of land for development leads to skyrocketing prices. The direct impact of NIMBY policies is the exacerbation of the housing affordability crisis, as less housing supply cannot meet the rising demand.
Moreover, NIMBY attitudes affect not only the number of new projects but also the types of homes that are developed. Smaller, bespoke projects may not suffice in addressing the needs for diverse housing options, such as affordable multifamily units. In areas where NIMBYism is particularly strong, the construction of large-scale, essential housing developments becomes virtually impossible, widening the homeownership gap as prices continue to increase without a subsequent increase in affordable housing supply.
Enhancing Construction Productivity through Innovation
Addressing the housing affordability crisis requires a concerted effort to enhance construction productivity, which involves embracing innovative building methods and technologies. Historical data illustrates a stark contrast between the construction sector and other industries, such as manufacturing, where productivity continued to rise post-1970. The decline in construction patents and R&D activity suggests that the sector has not kept pace with advancements that could drive down costs and increase output in housing development.
To rectify this, stakeholders including policymakers, builders, and communities must encourage innovative practices that streamline construction processes while respecting community concerns. This could involve relaxing certain land-use regulations to allow for larger-scale developments, or investing in modular and prefabricated housing that can be assembled more efficiently. By rekindling the spirit of innovation in housing construction, it may be possible to alleviate some of the pressures driving the housing affordability crisis.
The Homeownership Gap: A Growing Divide
The homeownership gap in the United States has widened dramatically in recent decades, particularly among different income and demographic groups. As housing costs soar and wage growth stagnates, many families find themselves shut out of the market entirely. The situation is particularly dire for younger generations and lower-income households, who are increasingly unable to build equity through homeownership. Factors such as rising student debt, stagnant wages, and the increase in living costs compound these challenges, leaving many to contend with a bleak financial future.
Moreover, this disparity reflects broader social inequities that have persisted for decades. Access to homeownership has historically been a pathway to wealth accumulation in the United States, thus the growing homeownership gap threatens economic mobility for affected demographics. To close this gap, targeted policy interventions and support programs are necessary, which could include expanding access to affordable housing, down payment assistance, and financial education to empower prospective buyers to navigate the housing market.
Cost Factors in Housing Development
In addition to land-use regulations and NIMBYism, various cost factors contribute to the rising price of housing. Labor shortages and increased material costs have been chronic issues within the construction industry, straining builders’ ability to deliver affordable homes. The combination of these costs creates a barrier to entry for many potential buyers, further complicating the existing housing affordability crisis. The challenge lies in finding solutions that can stabilize these costs while enabling more housing options.
One approach is to incentivize innovation in building materials and construction techniques that could lead to lower overall costs. For instance, the adoption of technology-driven construction methods or alternative materials could reduce reliance on traditional labor and resources, thereby lowering expenses. Stakeholders in the housing sector must collaborate to explore creative solutions that can address these cost factors, making homeownership more achievable for a larger segment of the population.
Navigating Housing Market Challenges with Policy Reform
Policymakers play a vital role in overcoming the challenges facing the housing market and addressing the housing affordability crisis. By reforming land-use regulations and removing unnecessary barriers to development, governments can create environments conducive to building more units. These reforms should aim to strike a balance between community interests and the need for increased housing supply, enabling the construction of larger developments that can accommodate growth.
In addition to regulatory changes, policymakers could explore financial incentives for builders who prioritize affordable housing projects. Tax credits, zoning allowances for higher density, and support for public-private partnerships can foster collaboration between different stakeholders, ultimately leading to a more vibrant housing market. With targeted policy reforms, it is possible to mitigate the challenges posed by NIMBYism and inadequate construction capacity, paving the way for solutions that create sustainable, affordable housing options.
Lessons from Historical Housing Developments
Studying historical housing developments provides valuable insights into effective strategies for addressing current housing market challenges. The successful mass production of homes in developments like Levittown during the mid-20th century illustrates the benefits of economies of scale. Such transformations were facilitated by a more collaborative regulatory environment, allowing large developments to thrive and meet the needs of growing populations.
However, the modern landscape is increasingly complicated by restrictive policies and local opposition to larger developments. Learning from past successes, stakeholders today must advocate for regulatory reforms that promote similar large-scale projects while considering the concerns of local communities. By looking back at these historical examples, planners and policymakers can inspire innovative housing strategies that respond to current market conditions and enhance affordability.
Future Directions for Affordable Housing Solutions
To tackle the multifaceted housing affordability crisis, the industry must focus on sustainable and innovative housing solutions that align with modern demands. Emphasizing eco-friendly construction practices, such as utilizing sustainable materials and energy-efficient designs, can resonate with contemporary buyers while addressing environmental concerns. These practices not only advocate for responsible development but also often result in long-term savings for homeowners.
Furthermore, collaborations among various sectors—government, private industry, and non-profit organizations—can lead to novel approaches to funding and supporting affordable housing initiatives. Coordinated efforts can create more cohesive responses to the housing crisis, ensuring that all households, regardless of income level, can access safe and affordable homes. Investing in these partnerships will be crucial for shaping a resilient housing market that can meet future challenges head-on.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors are contributing to the housing affordability crisis in the U.S.?
The housing affordability crisis in the U.S. can be attributed to several factors, including rising construction costs, restrictive land-use regulations, and NIMBY policies that hinder large-scale housing projects. These challenges limit the supply of affordable homes, pushing ownership out of reach for many Americans.
How do land-use regulations impact housing market challenges?
Land-use regulations significantly impact housing market challenges by restricting the size and scope of new developments. Such regulations often lead to smaller, bespoke housing projects, which reduce construction productivity and drive up costs, contributing to the ongoing housing affordability crisis.
What role do NIMBY policies play in the housing affordability crisis?
NIMBY policies exacerbate the housing affordability crisis by creating barriers to new construction. Homeowners often resist development in their neighborhoods, which leads to increased regulatory hurdles and limits the availability of affordable housing, further widening the homeownership gap.
How has construction productivity been affected by the housing affordability crisis?
The housing affordability crisis has led to declining construction productivity as land-use regulations and NIMBYism create obstacles for builders. With smaller projects becoming the norm, the economy of scale that once benefited housing construction has diminished, resulting in higher costs and fewer affordable housing options.
What is the connection between the homeownership gap and housing affordability?
The homeownership gap is closely linked to the housing affordability crisis, as rising home prices and limited housing supply make it increasingly difficult for lower and middle-income families to achieve homeownership. This gap is often exacerbated by construction productivity challenges and restrictive land-use policies.
How can addressing land-use regulations help alleviate the housing affordability crisis?
Addressing land-use regulations can help alleviate the housing affordability crisis by enabling more large-scale developments and reducing construction costs. By streamlining the approval process and encouraging mass-produced homes, it can promote increased housing supply, ultimately making homeownership more accessible.
In what ways have market challenges affected America’s approach to homebuilding?
Market challenges arising from the housing affordability crisis have shifted America’s approach to homebuilding, leading to smaller, less productive construction firms. These firms often struggle to innovate and implement cost-effective building practices, resulting in higher home prices and fewer affordable housing options.
What economic implications arise from the housing affordability crisis and declining construction productivity?
The housing affordability crisis and declining construction productivity have significant economic implications, including a massive intergenerational wealth transfer in housing. As younger generations face barriers to homeownership, wealth becomes concentrated among older homeowners, exacerbating economic disparities and limiting social mobility.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Tighter land-use controls negatively impact housing construction productivity. |
| Housing prices have doubled since 1960, making homeownership increasingly unaffordable. |
| NIMBY policies restrict large-scale housing projects, leading to smaller, less efficient builds. |
| Construction productivity stagnated since 1970, while other sectors, like automotive manufacturing, saw improvement. |
| The decline of large construction firms limits innovative practices and overall productivity in the housing sector. |
| Housing wealth has disproportionately benefited older homeowners, exacerbating generational wealth gaps. |
Summary
The housing affordability crisis poses a significant challenge in today’s economic landscape, affecting homeownership for a growing number of Americans. As land-use regulations and NIMBYism stifle construction productivity, the costs of new homes continue to soar. This analysis highlights the need for effective policy changes to foster innovation and efficiency in housing development, ultimately aiming to alleviate the burden of housing costs on future generations.